Introduction
The function of electrolytes often requires clarification in our pursuit of effective weight-loss techniques. Exploring the intricate relationship between electrolytes and weight management reveals intriguing physiological interactions within the body. Electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, magnesium, and other minerals, play vital roles in numerous bodily processes, from nerve impulses to muscular contractions.
While electrolytes are commonly associated with sports performance and hydration, their significance in weight loss is frequently overlooked. Understanding how these electrically charged minerals operate within the body can provide valuable insights into their potential assistance in achieving weight management goals. Electrolytes are essential to any weight loss plan, as they promote general health and well-being by facilitating cellular communication and maintaining fluid balance. Thus, many ponder: “Are electrolytes good for weight loss?”
Despite their importance, numerous myths and misconceptions surround electrolytes and their role in weight loss. One prevalent misconception is the belief that increasing electrolyte consumption alone can lead to noticeable weight loss. However, while crucial for sustaining metabolic processes, electrolytes are not a panacea for shedding excess weight.
Furthermore, there is a misconception that electrolyte supplements typically aid in weight loss. While certain electrolytes may support metabolism, excessive intake without medical supervision can lead to imbalances and potential health risks. For long-term effectiveness, electrolyte optimization must be approached as part of a comprehensive weight management plan that includes regular exercise, hydration, and a balanced diet.
As we delve deeper into the science of electrolytes and weight loss in the upcoming sections, we will explore their effects on metabolism, energy balance, and overall health. Understanding the intricate relationships between electrolytes and the body will enable us to develop practical strategies for maximizing their potential to help achieve weight loss objectives.
Understanding Electrolytes

Electrolytes, often known as the body’s electrical conductors, are a group of important minerals necessary for several physiological processes. Some main electrolytes are sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium, chloride, and phosphate. The body contains these minerals in its fluids, such as blood, urine, and sweat, where they combine to form electrically charged ions that can conduct electricity.
Different electrolytes have different purposes in the body. For example, sodium is essential for blood pressure regulation, fluid balance, and nerve impulse facilitation. Conversely, potassium helps with heart rhythm regulation, neuron function, and muscle contractions. While calcium is necessary for bone strength, muscle contractions, and nerve signaling, magnesium is essential for synthesizing energy, muscle function, and bone health.
The Vital Functions of Electrolytes in Human Physiology
Facilitating Muscle Contractions and Nerve Impulses: Electrical impulses that stimulate muscle contractions and nerve signaling are transmitted by electrolytes, especially sodium, potassium, and calcium. Insufficient electrolyte equilibrium can lead to nerve impairment, cramping, and muscle weakening.
Regulating Fluid Balance and Blood Pressure: Electrolytes are essential for preserving suitable fluid balance in the body’s cells; by controlling water flow across cell membranes, sodium and potassium aid in maintaining blood pressure, avoiding dehydration, and limiting fluid overload.
Supporting Immune Function and Cellular Communication: Electrolytes have a part in immune system health and cellular communication, in addition to their responsibilities in muscle and neuron function. For example, calcium supports cell-to-cell contact and signal transduction pathways necessary for numerous physiological functions, while magnesium is important in controlling immunological response.
Beyond just being a water source, electrolytes play various roles in human physiology, highlighting their importance. These necessary minerals are critical for sustaining general health, bolstering crucial body processes, and maximizing function in both physical and mental endeavors. Maintaining appropriate electrolyte balance and enhancing public health require consuming foods and drinks high in electrolytes.
Electrolyte Imbalance
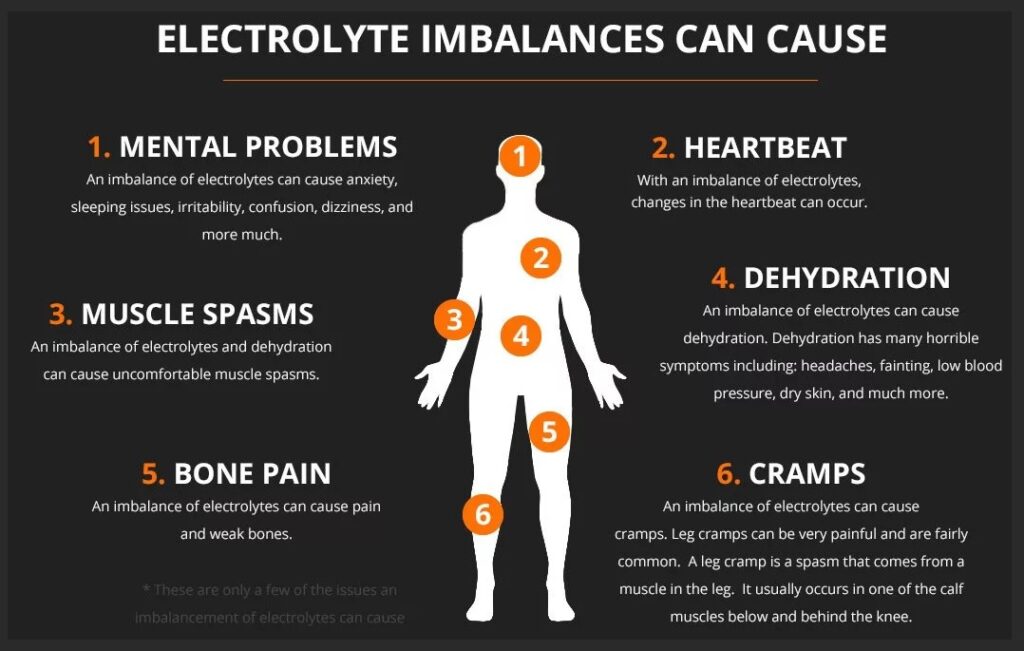
A. Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Electrolyte Imbalance
Muscle Cramps, Headaches, and Fatigue: Red Flags to Watch For
Various symptoms may indicate an electrolyte imbalance, making them important markers of underlying problems. Muscle cramps, which frequently happen during or after physical exercise, could mean a calcium, magnesium, or potassium deficit. Fatigue and headaches, especially when they coexist with muscle cramping, might indicate an electrolyte imbalance. Attention to these symptoms is important since they could mean making dietary or lifestyle changes to regain electrolyte balance.
B. Comprehending the Sources of Electrolyte Disproportion
Intense Exercise, Fasting, and Low-Carb Diets: Common Triggers
Prolonged fasting, high-intensity exercise, or low-carb diets can upset the body’s electrolyte balance. Exercise-induced sweating causes potassium and sodium loss, while prolonged fasting can lower magnesium levels. Similarly, low-carb diets can change the electrolyte balance by decreasing glycogen storage and raising potassium and salt output in the urine. It is imperative to be aware of these triggers to reduce the possibility of an electrolyte imbalance during weight loss efforts.
The Role of Processed Foods and Sodium-Potassium Balance
Processed foods can cause an electrolyte imbalance since they are frequently high in sodium and low in potassium, especially when consumed in excess. Potassium and salt levels out of balance throw off fluid balance, which can result in hypertension and other health issues. Therefore, to maintain normal electrolyte levels and support general health, it’s critical to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods rich in potassium, such as fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
Implications for Weight Loss and Metabolic Health
Weight loss and metabolic health are significantly impacted by electrolyte imbalance. Energy production, metabolic functions, and physical performance depend on maintaining an appropriate electrolyte balance. If imbalances are not corrected, they might make it more difficult to lose weight and raise the possibility of negative health effects. As a result, those starting weight loss programs should prioritize maintaining electrolyte balance through a healthy diet, enough water, and, when needed, thoughtful supplementation.
Electrolytes and Weight Loss
Although electrolytes are essential for many body processes, such as nerve and muscle impulses and muscular contractions, they are not a standalone weight reduction aid. Increased electrolyte consumption alone won’t significantly reduce weight, despite promises to the contrary. Weight loss is a complicated process that is impacted by several variables, such as metabolism, physical activity, food, and way of life in general. Although electrolytes can promote public health and well-being, it is best to think of them as a component of a long-term weight-management plan rather than a stop-all.
Mixed results have been found in the research on using electrolyte supplements in weight loss. When paired with a diet low in calories, some research indicates that electrolyte supplements may help with weight loss; however, other studies find no discernible difference. It’s critical to exercise caution when interpreting these results and consider individual variations in metabolism and supplement reaction. Furthermore, excessive electrolyte supplements might cause imbalances and negative health impacts, so it’s important to use caution.
Electrolytes are essential for metabolism and energy balance; they affect cellular activity, fluid management, and the absorption of nutrients. Maintaining metabolic efficiency and promoting physical performance during exercise requires optimal electrolyte levels. Further investigation is necessary to determine the precise pathways by which electrolytes impact weight reduction. Even though electrolytes might not be directly responsible for weight reduction, ensuring you get enough of them through a balanced diet and plenty of water can improve your general health and well-being, which are crucial elements of effective weight control techniques.
Integrating Electrolytes Into Your Weight Loss Journey
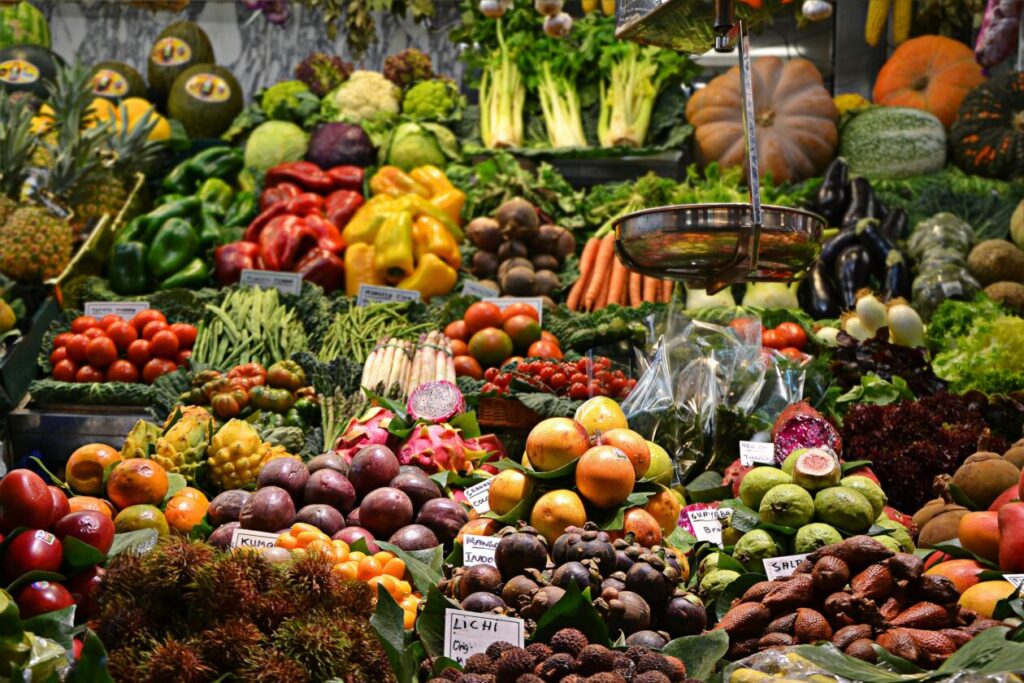

Fruits, Vegetables, and Whole Grains: Natural Sources of Potassium and Magnesium
A quick and easy approach to ensure you get the nutrients you need for weight control and overall health is to include foods high in electrolytes in your diet. Fruits high in potassium, an electrolyte essential for maintaining fluid balance and muscle function, include avocados, bananas, and oranges. In addition, magnesium, another necessary element that promotes energy generation and bone health, can be found in plants like spinach, broccoli, and sweet potatoes. Because whole grains like quinoa and oats also contain magnesium, they are beneficial additions to a balanced diet emphasizing electrolyte optimization.
DIY Electrolyte Water Recipes: Simple and Sugar-Free Solutions
Staying hydrated is imperative to assist weight loss attempts and preserve electrolyte balance. Make your electrolyte water with natural components to improve the absorption of electrolytes and hydration. A straightforward recipe calls for mixing water with a small amount of salt (to provide sodium) and citrus fruits (lime or lemon) to add flavor and vitamin C. You may add a dash of coconut water for potassium and hydration benefits. You may be sure you’re properly hydrating without additional sugars or artificial additives by eschewing sugary sports drinks and choosing DIY electrolyte water instead.
Navigating Electrolyte Supplementation Safely
Speak with medical professionals before taking electrolyte supplements for weight loss or general health considerations. For individualized advice about your unique requirements and state of health, speak with your physician or a qualified dietitian. Ensure your strategy is secure, efficient, and aligned with your health objectives by discussing electrolyte requirements and supplement alternatives with a healthcare provider. They can provide insightful information about the right kinds and amounts of electrolyte supplements depending on your age, health history, and eating preferences, among other things.
To maintain optimal health and optimize supplements, electrolyte level monitoring is essential. Frequent monitoring enables supplements to be adjusted as necessary to avoid deficiencies or imbalances. Your doctor can test your electrolyte levels and make recommendations based on the results. It is possible to reduce hazards and enhance general health by being vigilant about monitoring and modifying supplementation.
Even while electrolyte supplements have advantages when used properly, it’s important to be aware of potential hazards and restrictions. Specific groups may require caution or avoid particular forms of electrolyte supplements, such as those with underlying medical issues or those using medication. Your healthcare practitioner can assist in determining any risks or contraindications unique to your situation and offer tailored advice.
Overuse of supplements or excessive electrolyte consumption can also harm your health. Overconsumption of electrolytes can result in imbalances and dangerous consequences, including electrolyte poisoning or dehydration. It’s critical to prioritize getting your electrolytes from whole foods wherever feasible and avoid over-supplementation. Maintaining a balanced approach to electrolyte intake and supplementation can help you minimize risks and promote overall health and well-being.
Are Electrolytes Good for Weight Loss?
A. Answer in Short: Yes, electrolytes play a crucial role in weight loss efforts by promoting hydration, regulating fluid balance, and supporting metabolic functions. However, they are not a standalone solution for weight loss and must be part of a holistic approach that includes proper nutrition, regular exercise, and overall healthy lifestyle habits.
B. Answer in Depth with Value: Electrolytes are essential minerals that conduct electrical impulses in the body and play a vital role in various physiological functions, including muscle contractions, nerve signaling, and fluid balance. In weight loss, electrolytes are particularly important for maintaining hydration levels, as adequate hydration supports optimal metabolic function and may enhance the body’s ability to burn fat.
Potassium, magnesium, calcium, and sodium are key electrolytes contributing to overall health and well-being. Potassium, for example, helps regulate fluid balance and blood pressure, while magnesium supports muscle and nerve function. Calcium is essential for bone health and muscle contractions, while sodium helps maintain fluid balance and supports nerve signaling.
Incorporating electrolyte-rich foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, can help ensure you adequately intake these essential minerals. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day is crucial for supporting electrolyte balance and overall health. While electrolytes alone won’t lead to significant weight loss, optimizing their intake as part of a balanced diet and active lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being and support weight management goals.
FAQ Section: Electrolytes and Weight Loss
Q: Do electrolytes help weight loss?
A: Electrolytes don’t directly contribute to weight loss but are vital in maintaining hydration and supporting bodily functions that can indirectly impact weight management. Proper hydration facilitated by electrolytes can enhance metabolism and energy levels, which may aid in weight loss when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Q: Is it OK to drink electrolytes every day?
A: Drinking electrolytes daily is generally safe, especially if you’re active or live in a hot climate where you may lose electrolytes through sweat. However, choosing electrolyte sources wisely is essential, opting for natural options like fruits and vegetables or low-sugar electrolyte drinks to avoid excessive added sugars or artificial ingredients intake.
Q: How do you make electrolyte water for weight loss?
A: To make electrolyte water for weight loss, add electrolyte-rich foods like citrus fruits, cucumbers, or watermelon to your water. Alternatively, you can use electrolyte powders or tablets specifically formulated for hydration, ensuring they contain essential electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium without added sugars or unnecessary additives.
Q: What is the best hydration for weight loss?
A: The best hydration for weight loss involves drinking plenty of water throughout the day and incorporating electrolyte-rich fluids to replenish lost electrolytes, especially during exercise or increased sweating. Opting for water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables can also contribute to overall hydration and support weight loss goals.
Q: Can too many electrolytes cause weight gain?
A: Consuming too many electrolytes, particularly sugary or high-calorie beverages, can increase weight gain if they exceed your daily energy needs. It’s essential to balance electrolyte intake with overall calorie intake and consider the source of electrolytes to avoid excessive sugar or calorie consumption.
Q: Can I drink electrolytes on an empty stomach?
A: Yes, you can drink electrolytes on an empty stomach, especially if you’re engaging in physical activity or need to replenish electrolytes due to dehydration. However, be mindful of the type and concentration of electrolytes consumed to prevent discomfort or gastrointestinal issues.
Q: Do electrolytes affect metabolism?
A: Electrolytes play a role in supporting metabolism by facilitating cellular energy production and nutrient transport. Proper electrolyte balance can optimize metabolic function, possibly impacting weight management and overall energy expenditure.
Q: Do electrolytes add calories?
A: Pure electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium do not contain calories. However, electrolyte-containing beverages or supplements may contain added sugars or other calorie-containing ingredients. So, checking the label and choosing options with minimal added calories if you’re watching your calorie intake is essential.
Q: Does hydration help burn fat?
A: Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and can indirectly support fat loss by promoting optimal metabolism, energy levels, and physical performance. However, while proper hydration is crucial for overall well-being, it’s just one factor in a comprehensive weight loss plan that includes diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits.
Q: What do electrolytes do for the skin?
A: Electrolytes are essential for maintaining skin health and hydration. They help regulate fluid balance within skin cells, promote skin elasticity, and support the skin’s natural barrier function. Proper electrolyte balance can contribute to hydrated, healthy-looking skin.
Q: Do electrolytes help you sleep?
A: While electrolytes may not directly influence sleep, maintaining proper hydration and electrolyte balance can support overall health and well-being, contributing to better sleep quality. However, other factors, such as stress, lifestyle habits, and sleep hygiene, significantly affect sleep quality.
Q: Do electrolytes give you energy?
A: Electrolytes do not provide energy like carbohydrates or fats, but they are essential for energy production within the body. Proper electrolyte balance supports cellular function and nutrient transport, which can help optimize energy levels, especially during physical activity or increased exertion.
Q: How many electrolyte drinks per day?
A: The number of electrolyte drinks you need daily depends on various factors such as activity level, climate, and individual hydration needs. Aim to consume enough fluids to stay adequately hydrated, incorporating electrolyte-rich drinks as needed, especially during exercise or sweating.
Q: How much electrolytes do I need per day?
A: The recommended daily intake of electrolytes varies depending on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health. Adults should generally aim to consume adequate electrolytes through a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole foods, supplemented by electrolyte-containing beverages as needed.
Q: Is salt an electrolyte?
A: Yes, salt, or sodium chloride, is an electrolyte that plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions within the body. However, it’s essential to consume salt in moderation and balance it with other electrolytes like potassium and magnesium for optimal health.
Q: Do electrolytes help you lose water weight?
A: Electrolytes can help regulate fluid balance within the body, which may contribute to temporary fluctuations in water weight. However, relying solely on electrolytes for water weight loss is not advisable, as it’s essential to address underlying factors such as diet, hydration status, and overall health for sustainable weight management.
Q: Do electrolytes make you bloated?
A: While electrolytes do not typically cause bloating, consuming large amounts of electrolyte-containing beverages or supplements with added sugars or artificial ingredients may lead to bloating or gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals. Opting for natural sources of electrolytes and staying hydrated can help minimize bloating.
Q: What are the benefits of electrolytes?
A: Electrolytes play numerous essential roles in the body, including regulating fluid balance, supporting nerve and muscle function, maintaining pH balance, and facilitating nutrient absorption. They are vital for overall health and well-being, contributing to hydration, energy production, and cellular function.
Q: Does drinking electrolytes make you pee more?
A: Consuming electrolytes as part of a balanced diet or hydration regimen should only cause increased urination if you consume excessive amounts or have specific health conditions. Electrolytes help regulate fluid balance within the body, so adequate hydration is essential to support optimal urinary function and overall health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrolytes are critical in maintaining general health and well-being, which is necessary for long-term weight management even though they may not directly produce weight loss. You may optimize the electrolyte balance in your body and support your weight reduction objectives by including foods high in electrolytes in your diet, drinking enough water, and leading an active lifestyle. Nonetheless, electrolyte optimization must be approached as a component of a comprehensive plan that includes a healthy lifestyle, consistent exercise, and a balanced diet.
Let’s wrap up our talk about electrolytes and weight loss by empowering people to make educated choices regarding their electrolyte consumption and supplements. Those aware of the functions of electrolytes in the body and how they affect weight control can better make decisions supporting their overall well-being. Speaking with medical experts, such as physicians or qualified dietitians, can offer individualized advice on electrolyte requirements and supplement choices suited to specific situations.
Reference
Clinic, C. (2021). Electrolytes: Types, Purpose & Normal Levels. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/21790-electrolytes
West, H. (2018, October 24). Electrolytes: Definition, Functions, Imbalance and Sources. Healthline; Healthline Media. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/electrolytes#definition
Felman, A. (2020). Electrolytes: Uses, imbalance, and supplementation. Medicalnewstoday.com. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/153188
Pahl. (2021). Effect of rapid weight loss with supplemented fasting on serum electrolytes, lipids, and blood pressure. Journal of the National Medical Association, 80(7). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3404561/
Was this helpful?

Joseph Emb, RDN
Founder of StyleVitally.com | Registered Dietitian & Wellness Advocate
What I Cover:
I’m passionate about connecting nutrition science and everyday wellness to help people live healthier, more vibrant lives. I write about evidence-based nutrition, mindful eating, sustainable lifestyles, and holistic well-being at StyleVitally.com.
My Background:
The University of Texas in Austin, where I earned my Dietetics diploma, laid the groundwork for my nutrition and health career. My training and hands-on experience taught me the science and art of using nutrition to enhance health and well-being.
Professional Journey:
I’m an RDN with lots of experience. I’ve helped people seeking tailored nutritional recommendations in clinical settings and community outreach programs. My constant learning and professional development ensure that my recommendations are always based on the latest evidence.
Ethical Commitment:
My practice prioritizes integrity. My content is transparent and objective, following the most significant ethical standards. I can give my audience unbiased advice because I’m not affiliated with food businesses or industry associations. I want to help people make informed health decisions that match their values and ambitions.
Join Me on the Wellness Journey:
Join me on the path to vitality and well-being, whether facing nutritional issues, seeking sustainable lifestyle changes, or simply wanting a better, happier you. We’ll discover how diet, mindfulness, and holistic well-being can maximize your potential.










Leave a Reply
View Comments